In our previous article, we explained how Why Magento Still Wins for Complex Business LogicLearn how Magento’s layered architecture and modular design enable complex commerce logic, safe customization, and long-term scalability.Magento’s layered architecture is designed to support complex business workflows. For many businesses this typically means enabling pricing tiers, B2B flows, or localization. But for industries like biomedical, chemicals, and cross-border eCommerce, the challenge is often one of compliance.
A supplement that can be sold in one market may require front-end claim restrictions in another. A chemical compound may require license validation before purchase. A medical device might only be eligible for fulfilment from certified warehouses. These conditions shape how eCommerce needs to behave across regions, buyer types, and fulfillment networks.
TMO specializes in Magento development services that encodes regulated requirements such as eligibility rules, warehouse capabilities, and market-specific compliance.
In this article, we explore how Magento expresses compliance-driven constraints, drawing on our project experience developing platform architectures across industrial, medical, and specialized product categories.
5 Compliance Constraints in eCommerce
Specialized operations share a common requirement: the platform must model conditions that determine whether a product can be sold, how it can be fulfilled, and what information must appear on the storefront.
Because these constraints surface across several touchpoints (product display, checkout logic, fulfilment routing) each one often needs to be expressed differently within the platform:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Product-level | Rules tied to product composition, classification, or handling. | Ingredient restrictions, hazmat categories, dosage limits, temperature-controlled storage. |
| Buyer-level | Rules defining who is eligible to purchase specific products. | License validation, B2B-only access, age checks, professional verification. |
| Warehouse-level | Which nodes are eligible to fulfil certain items. | Cold-chain capability, hazmat certification, oversized handling, carrier availability. |
| Region-level | Market-specific eligibility, content, and compliance rules. | Restricted SKUs by country, claims suppression, required disclaimers or documentation. |
| Fulfillment-level | How items can be shipped or delivered. | Carrier restrictions, packaging requirements, prohibited routes, express-eligibility limits. |
To make things even more complicated, these constraints often intersect:
- A product may require temperature-controlled storage and can only ship from specific warehouses.
- A category of tools might be available only to verified B2B accounts and restricted to certain delivery methods.
- A region may permit the product but limit which claims can appear on the PDP or which carriers can be used.
In practice, the platform must often evaluate several conditions simultaneously—product attributes, buyer eligibility, regional rules, and warehouse capabilities—before deciding what to display, allow, or route.
The value of Magento’s architecture becomes most visible when operational rules dictate what customers see, how products are fulfilled, or which actions are allowed. The following are common scenarios where compliance and capability-driven logic can be leveraged:
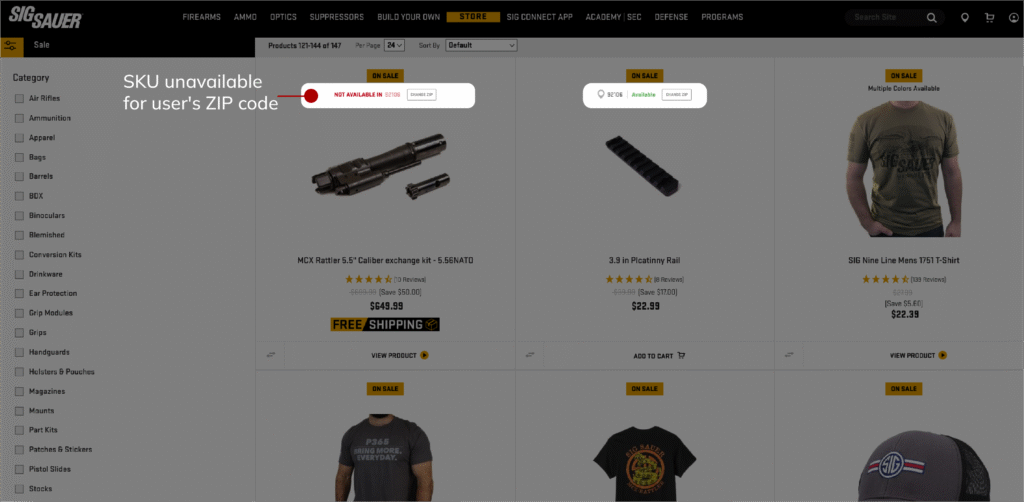
1. Region-Specific Product Eligibility
Commerce teams often need to determine whether certain products can be sold, displayed, or fulfilled in specific markets. Magento supports this through store-view configuration, attribute-based rules, and module-level logic that can evaluate regional restrictions before an item is surfaced to the shopper. Teams can conditionally expose SKUs, modify PDP content, or suppress certain claims based on geography without duplicating product records or hard-coding exceptions.
- Eligibility checks tied to region, country, or postal code
- Store-view-dependent PDP content or disclaimers
- Conditional catalog visibility rules based on regulatory obligations
2. Warehouse Capability–Based Routing
Some items can only be fulfilled from certified or appropriately equipped warehouses due to hazardous classifications, cold-chain requirements, oversized handling, or carrier restrictions. Magento’s inventory architecture allows warehouse-level attributes to be modeled and evaluated during allocation, ensuring that ineligible nodes are excluded from routing logic. This prevents fulfilment paths that violate operational or regulatory constraints.
- Warehouse attributes representing capabilities or certifications
- Allocation rules that evaluate stock and node eligibility simultaneously
- PDP-level surfacing of fulfilment node when relevant
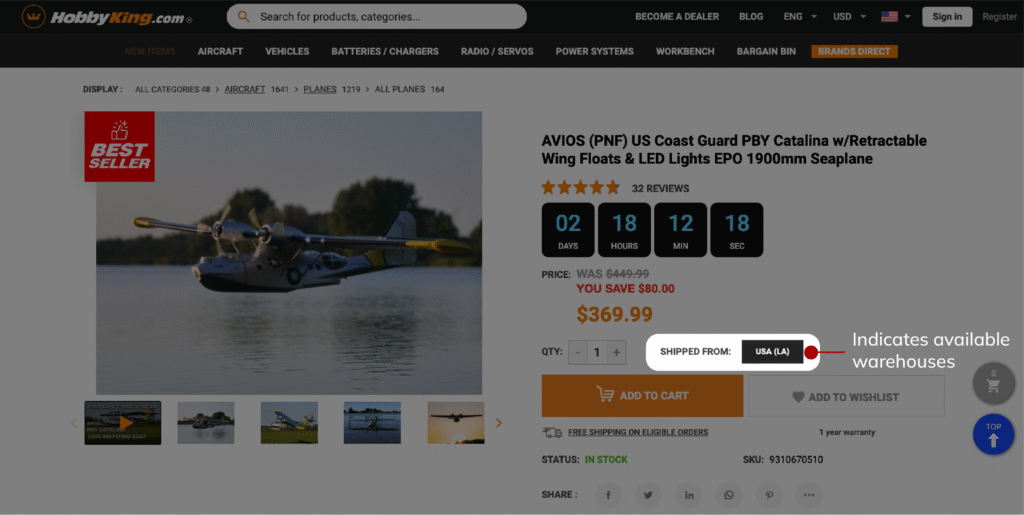
3. Buyer or Account-Based Access Control
Certain categories require customer-level verification before purchase, whether due to age restrictions, hazardous materials handling, or professional licensing. Magento enables account gating, controlled pricing visibility, and eligibility checks through customer attributes, custom modules, and checkout-level validation flows. This ensures that restricted products can only be purchased by verified buyers while maintaining a consistent experience for general users.
- Role-based access to SKUs or pricing
- Eligibility validation during account creation or checkout
- Attribute-driven gating for business, professional, or regulated buyers
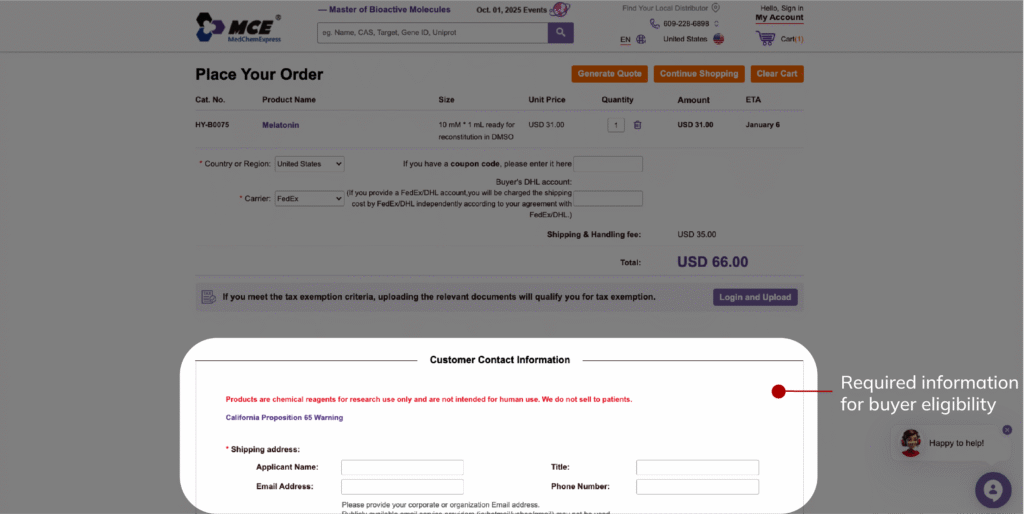
4. Regulated Content or Claims Control on PDPs
Regulations frequently dictate how product information must be presented in different markets, from ingredient declarations to hazard classifications to required documentation. Magento’s layered architecture makes it possible to adapt PDP content per region or compliance rule without duplicating catalog records. Disclaimers, documents, safety sheets, or controlled claims can be exposed or suppressed through module-level logic and store-view configuration.
- PDP-level content suppression or claim restrictions
- Dynamic exposure of safety sheets or documentation
- Store-view-specific labeling and messaging
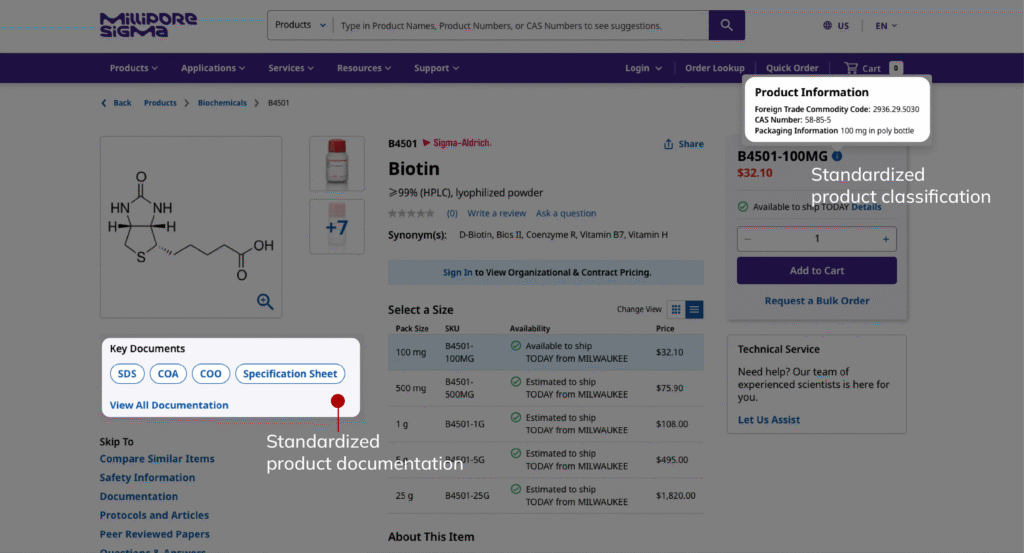
5. Carrier and Delivery Method Restrictions
Fulfilment rules often depend on product characteristics, whether an item is oversized, hazardous, temperature-controlled, or requires specialized carriers. Magento’s shipping logic can be extended to evaluate these constraints along with the customer’s location, ensuring only compliant delivery methods are displayed. When no permitted carriers exist, the platform can block online checkout or redirect the buyer to alternative fulfillment flows.
- Carrier-specific eligibility checks based on product attributes
- Blocking of shipping methods for hazardous or oversized goods
- Conditional routing to offline sales or specialized logistics partners
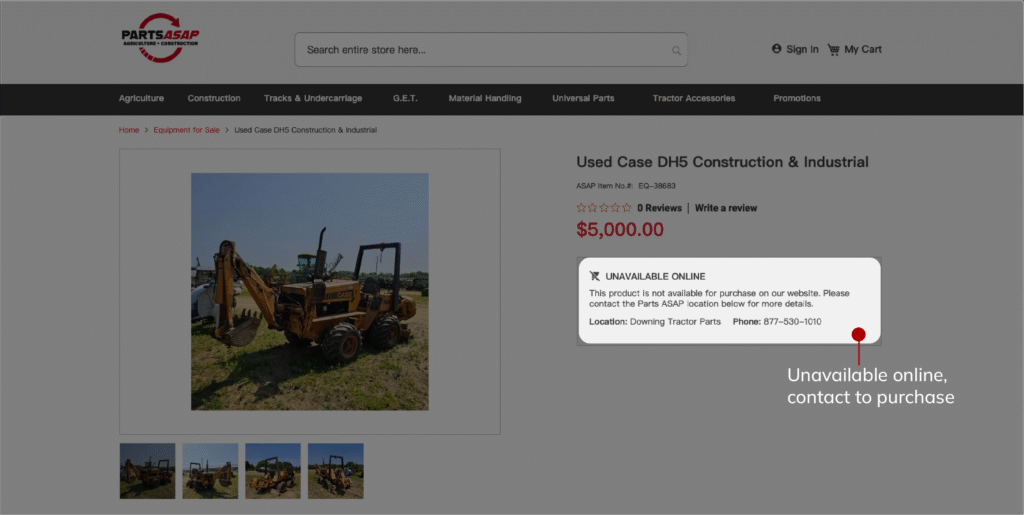
How to Define Your Compliance Rules Using Magento
Because Magento organizes business rules into modules, governance for each regulated or specialized area can be concentrated in a clearly defined place. When regulations change, a market is added, a third-party service is replaced, or the front-end is redesigned, the underlying logic can be updated within its module rather than across templates, connectors, or staging scripts. This is what keeps ongoing adjustments predictable and reduces the risk of hidden dependencies.
Designing a maintainable setup for regulated or specialized workflows typically follows a sequence of decisions that determine where rules live and how they behave:
- Define the constraints and where they belong: Identify which rules are product-level, buyer-level, warehouse-level, region-level, or fulfilment-level. This clarifies which Magento entities need additional attributes and which layers of the system participate in decisions.
- Establish the source of truth for each rule: Some data originates in ERP or WMS systems, for example hazardous classifications or warehouse capabilities. Other rules belong in Magento, such as catalog eligibility or store-view differences, while some require external services such as license validation or restricted-substance checks. Assigning ownership prevents duplicated or drifting compliance data.
- Design the decision module and its inputs: With constraints and data sources defined, the logic for “who can buy what, from where, and under which conditions” is implemented in a custom module. This module evaluates attributes and API responses, then determines outcomes such as product visibility, fulfilment eligibility, or permitted delivery methods.
- Integrate external checks through stable APIs: When validation depends on third-party services, Magento’s APIs allow the compliance module to call those services from the domain layer, not the front-end. This keeps the architecture clean and makes it straightforward to replace or update providers without redesigning the flow.
- Ensure the front-end reflects only the outcomes: The storefront should not carry compliance logic. It displays which products are available, which actions are permitted, and which delivery options apply. This allows design changes, channel changes, or headless implementations without re-implementing regulatory rules.
- Assign governance and operational ownership: Architecture only works if someone maintains the rules. As regulations, product lines, or market strategies evolve, module-level governance ensures the implementation stays accurate and stable.
Taken together, this process allows Magento to act as the architectural layer where compliance logic is expressed cleanly, structured, traceable, and ready to adapt as conditions change.
Build Compliant Workflows with Magento and TMO
Regulated and specialized industries impose rules that evolve over time: new markets open, product classifications shift, warehouse capabilities change, and external validation services are replaced or updated. Magento’s value in this environment lies in its ability to express these rules within structured modules rather than across front-end code, plugins, or one-off integrations. That separation is what keeps compliance requirements maintainable as complexity grows.
However, long-term stability ultimately depends on how the modules are designed. Clean boundaries, clear data ownership, and well-structured decision logic determine whether the system absorbs change or accumulates technical debt. Good architecture makes regulatory adaptation routine, while poor architecture makes it expensive.
At TMO, we’ve built Magento implementations for industries where constraints are not optional, from ingredient-restricted products to specialized fulfillment networks and multi-market compliance demands. Our Adobe-certified team and experience across diverse tech stacks allow us to design module-level architectures that remain predictable as regulations evolve, upstream systems change, or new markets come online.
If you're preparing to launch a regulated product line, planning a multi-market expansion, or assessing whether Magento can support your compliance workflows, reach out to TMO for a personalized discussion